In the complex human immune system, the interleukin (IL) family plays a pivotal role. Among them, interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a key member involved not only in immune regulation, hematopoiesis, and inflammatory processes, but also closely associated with the onset and progression of various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammation, and cancers.
Introduction to IL-6
The IL-6 family is a large group of cytokines comprising IL-6, IL-11, CNTF, LIF, OSM, CT-1, CLC, NPN, IL-27, IL-31, and others. These cytokines share structural similarities and partially overlapping mechanisms of action. As a representative member, IL-6 has a molecular weight of 19–28 kDa and consists of two glycoprotein chains (α and β). It exerts broad biological effects by binding to IL-6 receptors (IL-6R) expressed on various cell types.
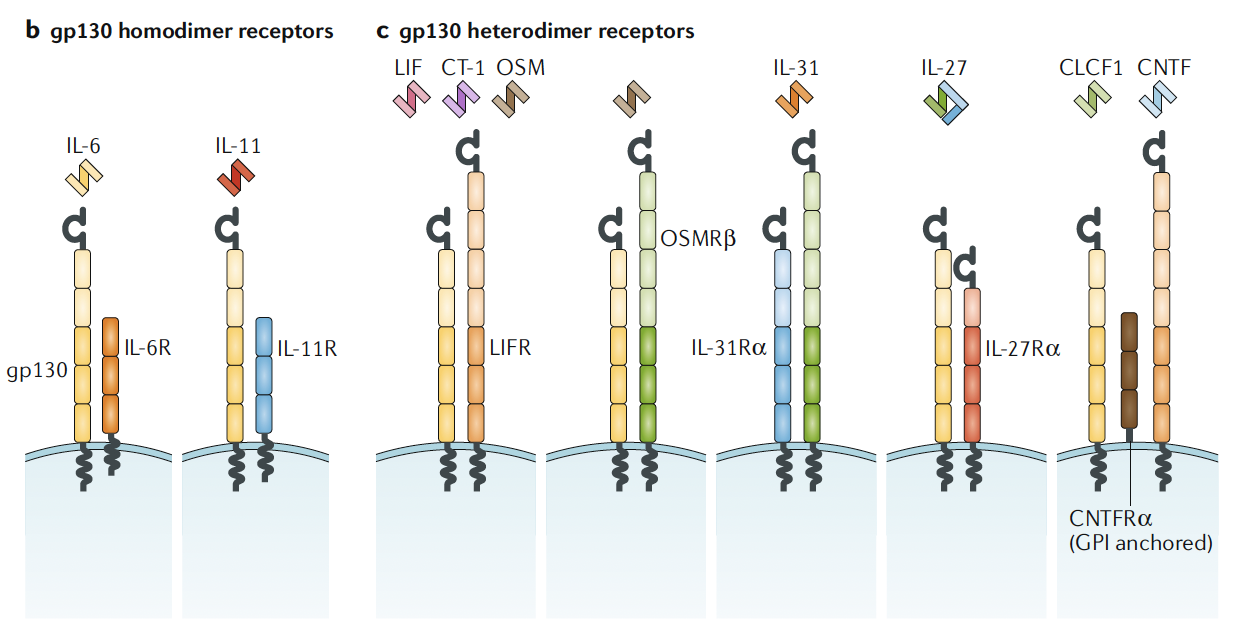
Figure 1. The Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Cytokine Family [1]
IL-6 Signaling Pathways
IL-6 mediates its effects primarily through three signaling mechanisms:
- Classic Signaling (Anti-inflammatory)
IL-6 binds to its membrane-bound receptor (mIL-6R), forming a complex that associates with the membrane protein gp130, which then activates downstream signaling cascades. - Trans-Signaling (Pro-inflammatory)
The soluble form of IL-6R (sIL-6R) binds IL-6 with similar affinity to mIL-6R. The IL-6/sIL-6R complex interacts with gp130, triggering intracellular signaling in cells lacking mIL-6R, thus expanding the range of target cells. - Trans-Presentation
In dendritic cells (DCs), IL-6 binds to mIL-6R intracellularly and is transported to the cell surface, where the complex engages gp130 on target cells. This activates pathways such as PI3K/AKT and induces Th17 cell differentiation, contributing to inflammation.
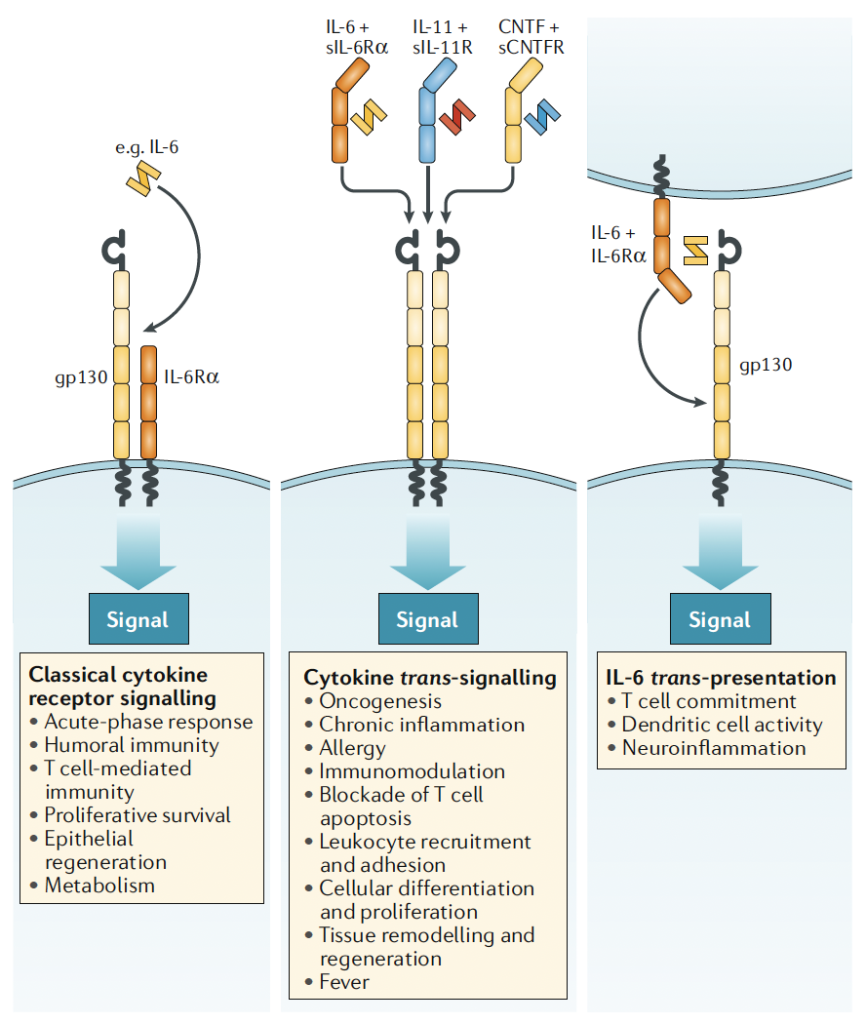
Figure 2. IL-6 signaling pathways [1]
IL-6 in Disease Pathogenesis
Cytokines of the IL-6 family exert complex pathological roles across a variety of diseases. In autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis, dysregulated IL-6 signaling is implicated in disease initiation and progression. In cancer, IL-6 family cytokines contribute to tumor growth and metastasis and may promote the formation of a tumor-supportive microenvironment and immune evasion. Thus, targeted therapies against IL-6 family cytokines are becoming a major focus in treating inflammatory diseases and malignancies.
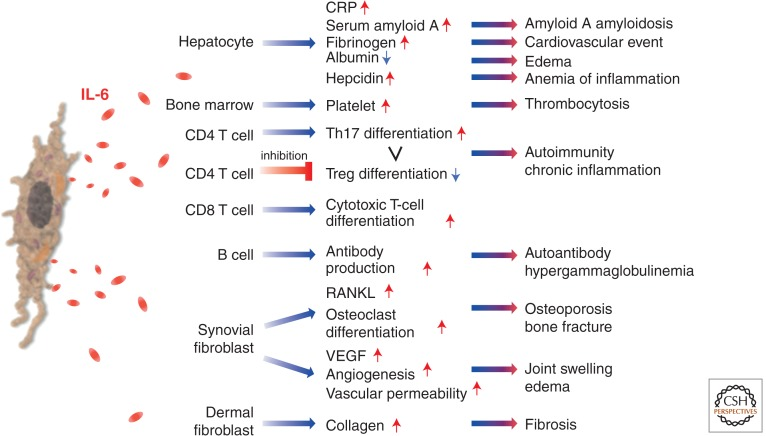
Figure 3. IL-6 roles in inflammation, immunity, and disease [2]
IL-6 Humanized Mouse Models by GenoBioTX
GenoBioTX has long been committed to developing humanized models for drug target validation. The IL-6/IL-6R humanized mouse model (hIL6/hIL6R, Catalog No.: NM-HU-190025) developed in-house provides a powerful tool for evaluating drug efficacy and safety related to IL-6.
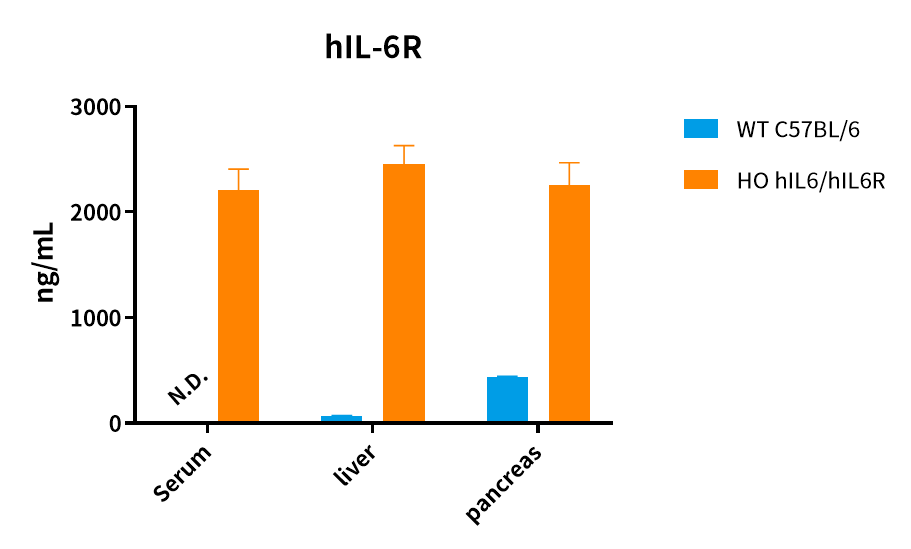
Figure 4. ELISA detection of human IL-6R expression in hIL6/hIL6R mice.
Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Model and Therapeutic Evaluation in hIL6/hIL6R Mice
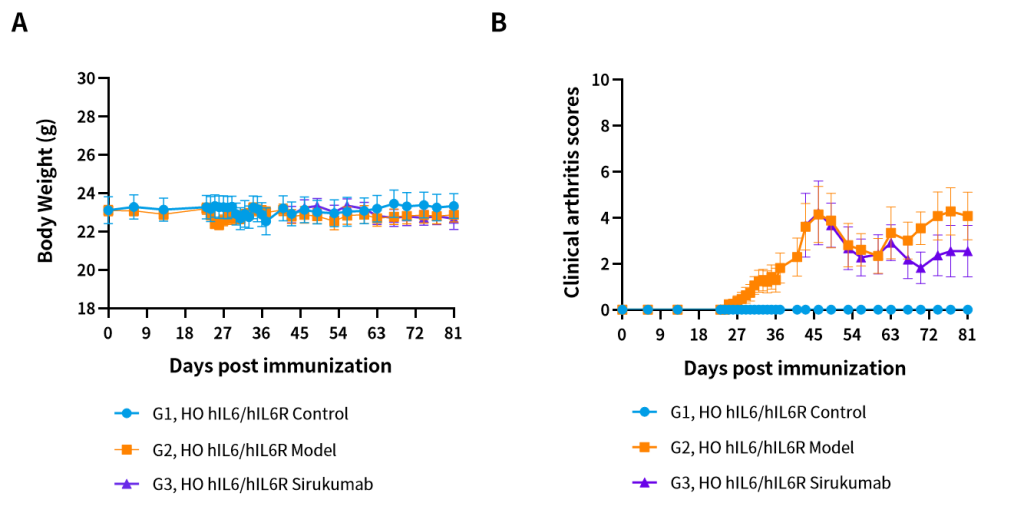
Figure 5. Therapeutic effects of Sirukumab in hIL6/hIL6R CIA model mice: (A) Body weight; (B) Clinical score.
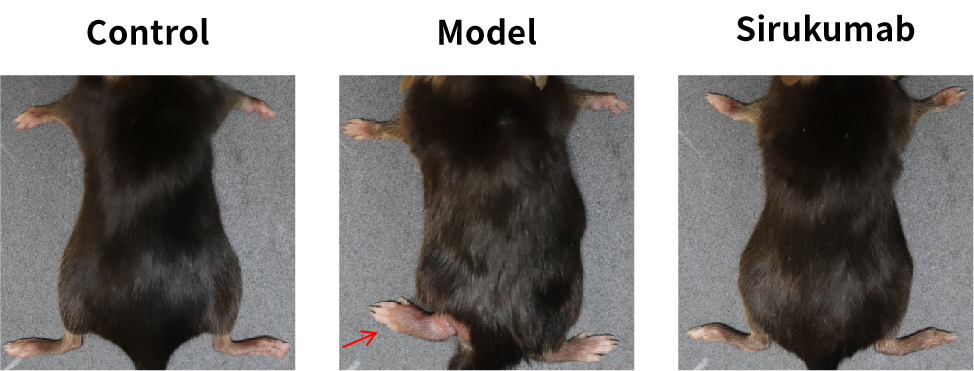
Figure 6. Representative hind limb joint images from different treatment groups.
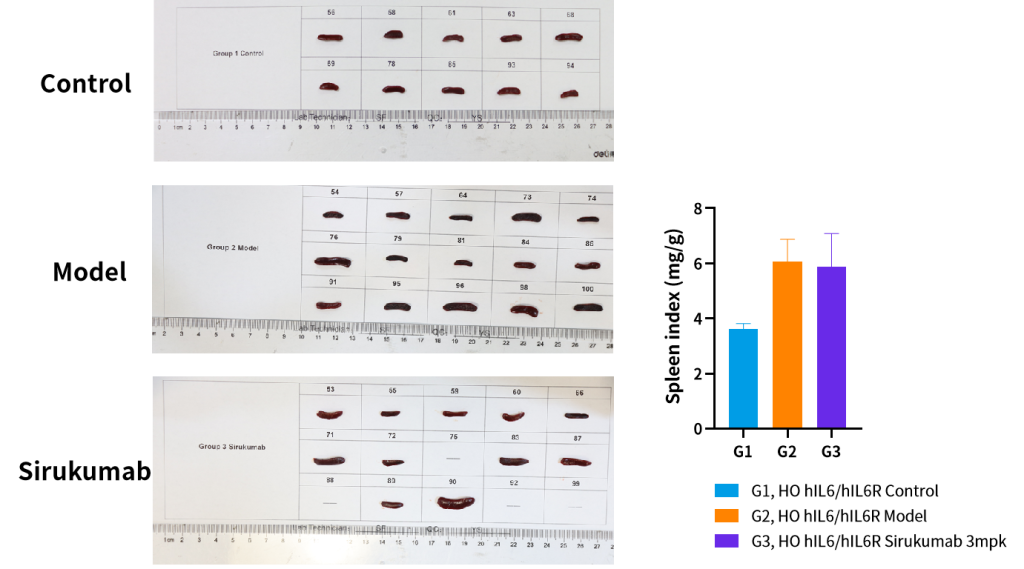
Figure 7. Efficacy of Sirukumab in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Model Using hIL6/hIL6R Humanized Mice
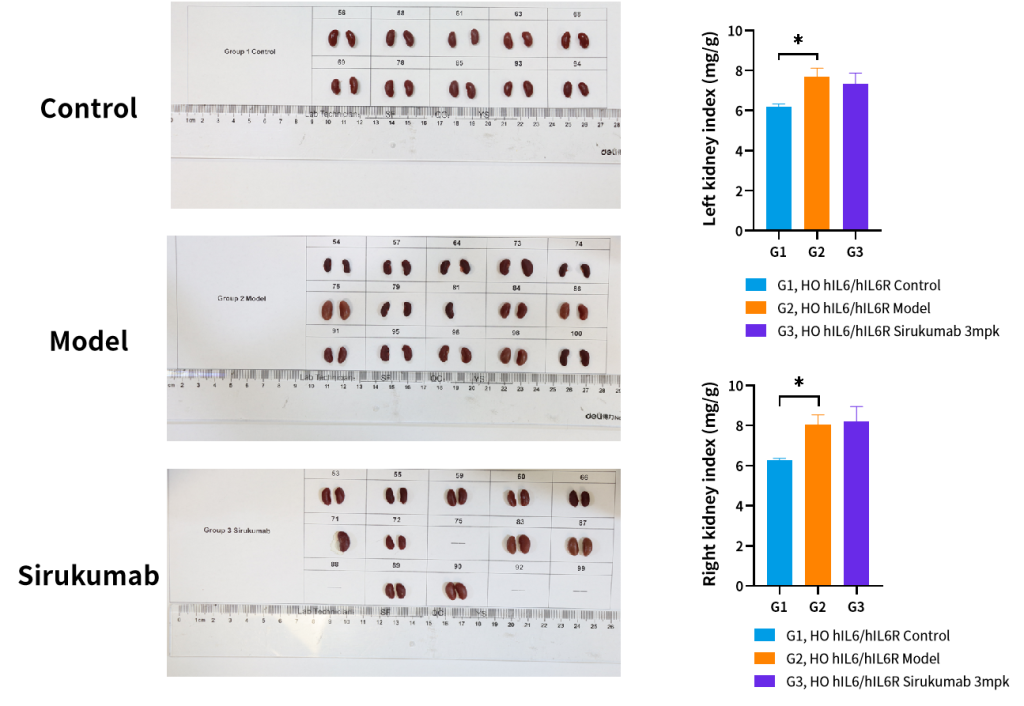
Figure 8. Efficacy of Sirukumab in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Model in hIL6/hIL6R Humanized Mice

Figure 9. Efficacy of Sirukumab in the Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Model in hIL6/hIL6R Humanized Mice: Representative micro-CT Images of Ankle Joints from Each Treatment Group
In addition to the above, GenoBioTX offers a range of other IL-6 target humanized mouse models to accelerate new drug development.
| Cat No. | Strain Name |
| NM-HU-18017 | hIL6 |
| NM-HU-190025 | hIL6/hIL6R |
| NM-HU-220427 | hIL6/hIL6R (M-NSG) |
| NM-HU-00044 | hIL6R |
| NM-HU-204980 | hIL6ST |
| NM-HU-200008 | hIL31 |
| NM-HU-204981 | hIL11 |
| NM-HU-210372 | hIL11/hIL11RA |
| NM-HU-204982 | hIL11RA |
Reference:
[1] Jones, S. A., & Jenkins, B. J. (2018). Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nature reviews. Immunology, 18(12), 773–789. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7
[2] 2.Tanaka, T., Narazaki, M., & Kishimoto, T. (2014). IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 6(10), a016295. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016295